Greenspan: Greek default could be Achilles’ heel for U.S. economy
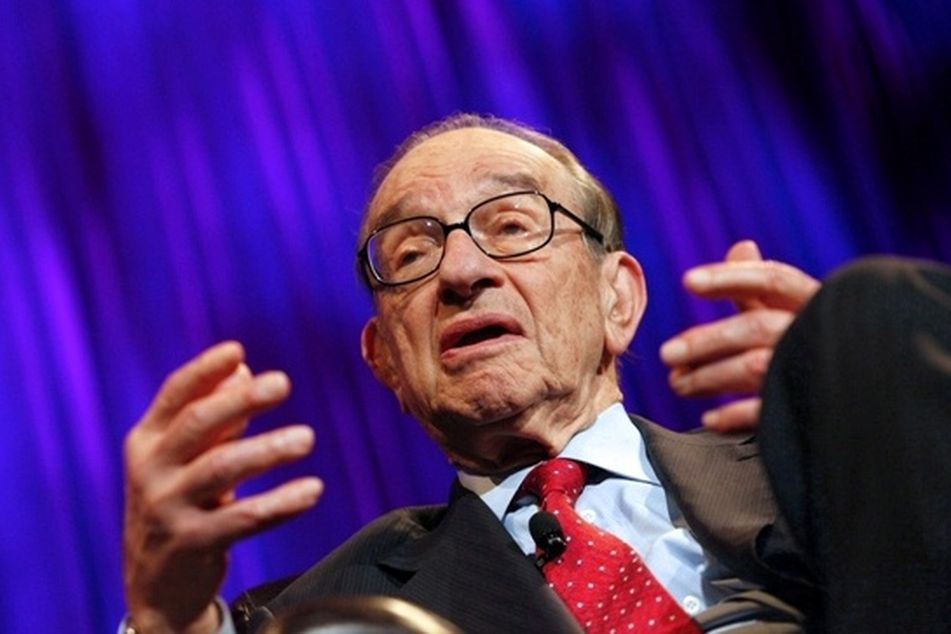

Alan Greenspan, former Federal Reserve chairman, said a default by Greece is “almost certain” and could help drive the U.S. economy into recession.
Alan Greenspan, former Federal Reserve chairman, said a default by Greece is “almost certain” and could help drive the U.S. economy into recession.
“The problem you have is that it’s extremely unlikely the political system will work” in a way that solves Greece’s crisis, Greenspan, 85, said in an interview yesterday with Charlie Rose in New York. “The chances of Greece not defaulting are very small.”
Greek government bonds slumped, pushing the yield on the two-year note above 30 percent for the first time, as Prime Minister George Papandreou’s failure to win support for more austerity fueled speculation the European country will fail to meet its obligations. More than 20,000 people protested in Athens this week against wage reductions and tax increases, with police using tear gas on crowds and strikes paralyzing ports, banks, hospitals and state-run companies.
The chances of Greece defaulting are “so high that you almost have to say there’s no way out,” said Greenspan, who ran the central bank from 1987 to 2006. That may leave some U.S. banks “up against the wall.”
Greece’s debt crisis has the potential to push the U.S. into another recession, Greenspan said. Without the Greek issue, “the probability is quite low” of a U.S. recession, he said.
“There’s no momentum in the system that suggests to me that we are about to go into a double-dip,” Greenspan said.
Economic data released today show confidence in the expansion eroding among Americans and businesses, as unemployment remains above 9 percent.
U.S. Debt Limit
The U.S. recovery is being hindered by apprehension among businesses over the long-term outlook, and there’s nothing more for Fed policy makers to do, Greenspan said.
U.S. lawmakers are wrangling over spending cuts and budget reforms as they seek an agreement to increase the $14.3 trillion debt limit before Aug. 2, the date on which the Treasury Department said it will have exhausted its borrowing authority.
The U.S. debt issue is becoming “horrendously dangerous,” said Greenspan, who added he doubts lawmakers have another year or two to solve it.
After leaving the Fed, the former chairman founded the consulting firm Greenspan Associates and became a consultant or adviser to Deutsche Bank AG, Pacific Investment Management Co. and Paulson & Co., a hedge-fund firm that profited from the collapse of the U.S. subprime-mortgage market.
Greenspan, appointed Fed chairman by Republican President Ronald Reagan, was once described as “the greatest central banker who ever lived” by economist Alan Blinder, the central bank’s former vice chairman.
He has since been blamed for contributing to the U.S. financial crisis by keeping interest rates low for too long and failing to regulate the mortgage market, according to critics including Allan Meltzer, a professor at Carnegie Mellon University in Pittsburgh, and members of the Financial Crisis Inquiry Commission.
–Bloomberg News–
Learn more about reprints and licensing for this article.